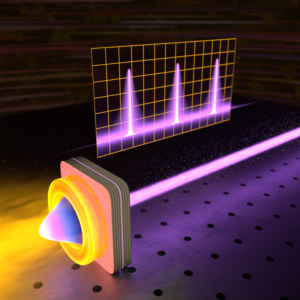
Illustration of a trapped polariton condensate giving rise to the laser emission with an ultra-narrow spectral peak detected by a scanning Fabry–Pérot interferometer.
Ground-breaking research revealed the ultra-narrow linewidth of a novel type of laser that operates without population inversion.
Exciton-polariton lasers, renowned for their low-power operation, have long tantalised researchers with their promise for practical low-energy applications.
However, until now, a clean measurement of the laser’s linewidth, or spectral purity, has remained elusive.
“The spectral purity is one of the defining characteristics of a laser, which tells how close the individual photon energies or frequencies are to each other,” says ARC DECRA Fellow Dr Eliezer Estrecho.
A laser’s spectral purity is quantified by a measure known as linewidth.
The challenge in measuring the linewidth arise from the strong interaction of exciton-polaritons with each other and the environment, leading to significant fluctuations. Previous measurements needed to average over long periods of time to determine the linewidth, which leads to artificially enlarged linewidth.
To avoid averaging, the researchers employed a new, precise measurement method using a commercial scanning Fabry–Pérot interferometer.
“The interferometer enabled unprecedented levels of detail that was obscured in previous measurements using conventional techniques,” commented FLEET PhD student, Bianca Rae Fabricante.
The experiments revealed that, contrary to previous assumptions, the laser can maintain an ultra-narrow linewidth of 56 MHz or 0.24 µeV, ten times smaller than previously published results.
This places polariton lasers on par with the current leading technology VCSELS, which is widely used in facial recognition and augmented reality.
“Polariton lasers are potentially better than VCSELS for low-energy applications since they can operate at lower powers,” says FLEET Research Fellow Dr Mateusz Król.
The low-power operation is possible because these lasers derive their coherent emission from a macroscopically populated coherent quantum state – a bosonic condensate of exciton-polaritons. Unlike conventional lasers that rely on population inversion, the onset of lasing can be achieved at lower pump powers.
The study also challenges conventional wisdom by demonstrating that the overlap between the coherent exciton-polariton condensate and an incoherent reservoir of particles does not significantly broaden the linewidth.
This is good news since the incoherent reservoir always coexists with exciton-polaritons and was initially thought to inevitably introduce significant noise to the polariton laser. The study reveals that as long as the polaritons are confined or trapped, the effect is weak.
What’s next…
“Our work not only pushes the boundaries of exciton-polariton laser technology but also opens up new avenues for utilising exciton-polaritons for classical and quantum computing,” remarked Dr Estrecho.
A narrow linewidth means a long coherence time, in this case at least 5.7 nanoseconds.
This is enough time to perform, in principle, thousands of successive operations on the source of the laser, a macroscopic quantum state of condensed exciton-polaritons. This is a critical step for quantum information processing applications of polaritons.
The study’s impact extends far beyond the realm of exciton-polaritons, offering invaluable insights into broader fields. Drawing parallels with photonic and atom lasers, the research paves the way for a deeper understanding of noise spectra and spectral properties critical for various applications.
“Ever since their discovery, low-threshold polariton lasers that do not require a population inversion, have been waiting for practical applications. Our study suggests that such applications can be broader than previously thought,” added FLEET Theme 2 Leader Prof. Elena Ostrovskaya.
The study
“Narrow-linewidth exciton-polariton laser” was published in Optica in June 2024. (DOI: 10.1364/OPTICA.525961)
The authors acknowledge funding from the Australian Research Council (DECRA and Centre of Excellence Programs) and Schmidt Science Fellowship.
Measurements were performed in the Polariton BEC Research Group at the Research School of Physics, Australian National University, which investigates macroscopic quantum states such as Bose-Einstein condensation (BEC) of exciton-polaritons, low-dimensional physics, non-equilibrium physics, and other fundamental investigations towards future polaritonic devices.