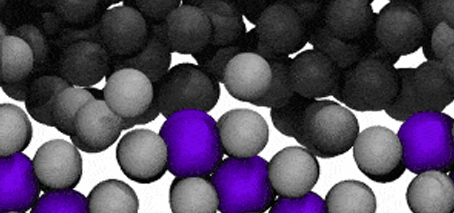
The boundary between solid metal and liquid metal can be much less ‘solid’ than we ever suspected. RMIT researchers have discovered that the liquid-solid boundary can fluctuate back and forth, with metallic atoms near the surface breaking free from their crystal lattice. Observing a metal-alloy mass solidifying in a sea of liquid metal, the team was able to observe a …
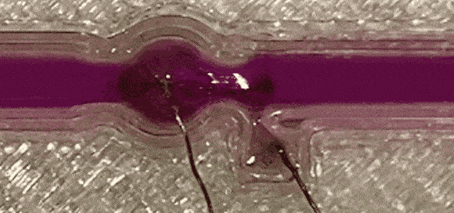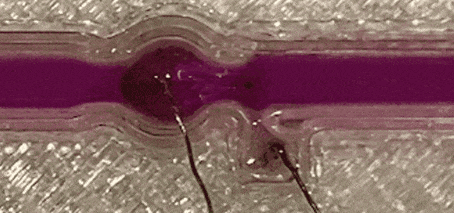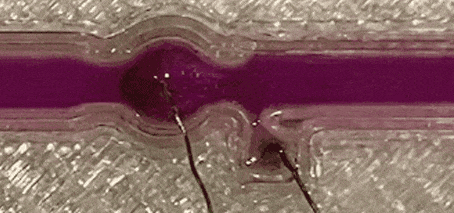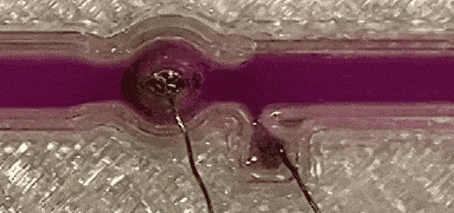
Liquid-metal transfer from anode to cathode without short circuiting
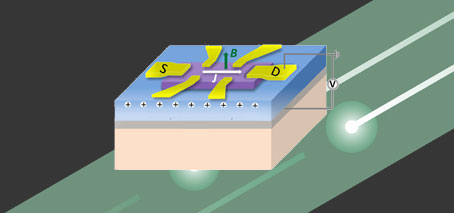
University of Wollongong researchers achieved a significant milestone in novel soft-matter transport by demonstrating the transfer of liquid metal from an anode to a cathode without creating a short circuit, defying conventional expectations. The team led by Prof Xiaolin Wang unveils a method where liquid-metal (specifically gallium-based, room temperature liquid metal) anodes can flow towards cathodes with a small electrical …
Pioneering study achieves liquid-metal transfer via electrical current
first published at the University of Wollongong In a ground-breaking discovery, University of Wollongong (UOW) researchers, have reached a new milestone in soft-matter transport. The team, based at the UOW node of the ARC Center of Excellence in Future Low Energy Electronics Technology (FLEET), has successfully demonstrated the transfer of liquid metal from an anode to a cathode without short circuiting, defying …
Infrastructure funding for FLEET researchers
This month’s ARC infrastructure funding round saw FLEET researchers across five universities on teams awarded additional funding towards research facilities, including significant new imaging resources in South Australia and NSW. Pankaj Sharma, initially a FLEET Research Fellow at UNSW and now a Centre AI at Flinders University (South Australia), will help develop new, state-of-the-art atomic force microscopy (AFM) facilities for the …
Space has gotten small with metallic, planet-like nanodroplets
Homogenous liquid-metal nanodroplets achieved with high-temperature molten salt Australian researchers put planets in the palm of the hand Liquid metal, planet-like nanodroplets are successfully formed with a new technique developed at RMIT University, Australia. Like our own Planet Earth, the nanodroplets feature an outer ‘crust’, a liquid metal ‘mantle’, and a solid ‘core’. The solid intermetallic core is the key …
Tiny device mimics human vision and memory abilities
First published at RMIT Researchers have created a small device that ‘sees’ and creates memories in a similar way to humans, in a promising step towards one day having applications that can make rapid, complex decisions such as in self-driving cars. The neuromorphic invention is a single chip enabled by a sensing element, doped indium oxide, that is thousands of …
Combining irradiation and lithography to engineer advanced conducting materials
A process has been developed to engineer nanoscale arrays of conducting channels for advanced scalable electronic circuitry Using ion implantation and lithography, investigators created patterns of topological surface edge states on a topological material that made the surface edges conductive while the bulk layer beneath remained an insulator Low energy ion implantation, neutron and X-ray reflectometry techniques at ANSTO supported …
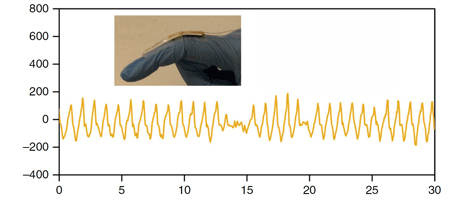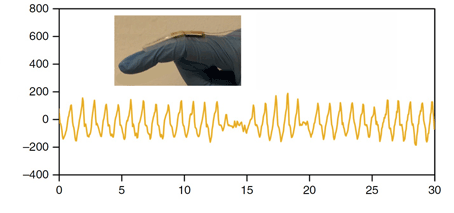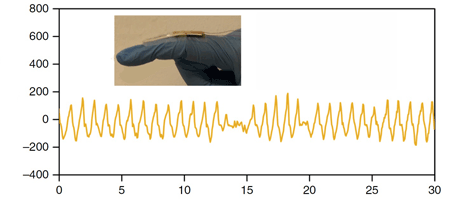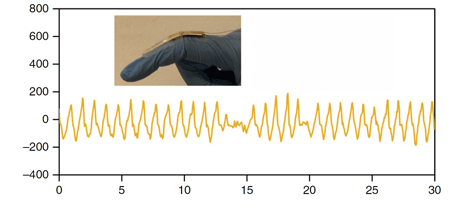
Let it snow inside liquid metals
Liquid metals are enigmatic metallic solvents. A new UNSW-led study of metallic crystals growing in a liquid metal solvent finds similarities and differences between liquid-metal solvents and more-familiar crystal-growth environments (such as water or the atmosphere) in which snowflakes or crystals of dissolved substances form. We can dissolve a large amount of sugar in water at high temperatures. But as …
A shield for 2D materials that adds vibrations to reduce vibration problems
Ultra-thin, liquid-metal-printed oxide can improve performance of your transistor by suppressing vibrational resistance Counterintuitively, this occurs by adding extra phonons (vibrations) into the system This oxide can protect your transistor against further processing Monash University researchers have demonstrated a new, counterintuitive way to protect atomically-thin electronics – adding vibrations, to reduce vibrations. By ‘squeezing’ a thin droplet of liquid gallium, …
FLEET translation: extending LED device lifetime with liquid-metal printed oxides
2D oxide-based LED encapsulation extending device lifetime FLEET translation funding is supporting the next step in a liquid-metal printing application with significant commercial promise, in a project being led by RMIT PhD candidate Patjaree Aukarasereenont. Light-emitting diodes (LEDs) play a crucial role in modern society – from mobile phones to LED billboards and home lighting, LEDs are ubiquitous. There are, …
A new era of two-dimensional ferroelectrics
A UNSW/Flinders University paper published recently in Nature Reviews Materials presents an exciting overview of the emerging field of 2D ferroelectric materials with layered van-der-Waals crystal structures: a novel class of low-dimensional materials that is highly interesting for future nanoelectronics. Future applications include ultra-low energy electronics, high-performance, non-volatile data-storage, high-response optoelectronics, and flexible (energy-harvesting or wearable) electronics. Structurally different from …
Manipulating interlayer magnetic coupling in van der Waals heterostructures
Electrical control of exchange bias effect in FePS3-Fe5GeTe2 van der Waals heterostructures via proton intercalations A RMIT-led international collaboration published this week has observed, for the first time, electric gate-controlled exchange-bias effect in van der Waals (vdW) heterostructures, offering a promising platform for future energy-efficient, beyond-CMOS electronics. The exchange-bias (EB) effect, which originates from interlayer magnetic coupling, has played a …
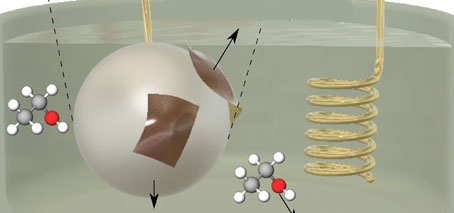
Liquid platinum at room temperature: The ‘cool’ catalyst for a sustainable revolution in industrial chemistry
In an Exciton Science/FLEET study, researchers have been able to use trace amounts of liquid platinum to create cheap and highly efficient chemical reactions at low temperatures, opening a pathway to dramatic emissions reductions in crucial industries. When combined with liquid gallium, the amounts of platinum required are small enough to significantly extend the earth’s reserves of this valuable metal, …
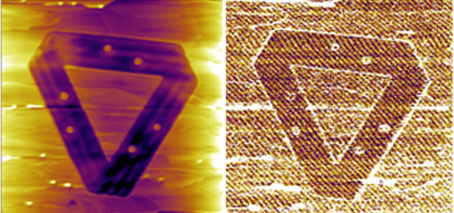
Liquid metals, surface patterns, and the Romance of the Three Kingdoms
“The long divided, must unite; long united, must divide. Thus it has ever been.” The opening lines of the great Chinese historical novel Romance of the Three Kingdoms condense its complex and spectacular stories into a coherent pattern, that is, power blocs divide and unite cyclically in turbulent battle years. A good philosophy or theorem has general implications. Now, published …
No more moving parts: Liquid metal enabled chemical reactors
Liquid-metal machines could wipe out maintenance issues for continuous flow reactors. Metals that are liquid at room temperature, such as gallium and its alloys, are attractive materials due to their unique electrical, thermal and fluidic properties. In a study published today, a research team led by UNSW, Sydney has shown that liquid metals can offer their characteristics to the pharmaceutical and chemical …
World record broken for thinnest X-ray detector ever created
Highly sensitive and with a rapid response time, the new X-ray detector is less than 10 nanometres thick and could potentially lead to real-time imaging of cellular biology. Exciton Science and FLEET researchers have used tin mono-sulfide (SnS) nanosheets to create the thinnest X-ray detector ever made, potentially enabling real-time imaging of cellular biology. X-ray detectors are tools that allow …
Quantifying spin in WTe2 for future spintronics
Spin-momentum locking induced anisotropic magnetoresistance in monolayer WTe2 Determining spin quantization axis, an essential element for fabricating spintronic devices, in 2D topological insulator WTe2 by measuring anisotropic magnetoresistance A RMIT-led, international collaboration published this week has observed large in-plane anisotropic magnetoresistance (AMR) in a quantum spin Hall insulator and the spin quantization axis of the edge states can be well-defined. …
Stress can be good for you: enhancing piezoelectric properties under pressure
Innovative epitaxy technique creates a new phase of the popular multiferroic BiFeO3 Stress enhances the properties of a promising material for future technologies. UNSW researchers find a new exotic state of one of the most promising multiferroic materials, with exciting implications for future technologies using these enhanced properties. Combining a careful balance of thin-film strain, distortion, and thickness, the team …
Elements in liquid metals compete to win the surface
Some alloys are in the liquid state at or near room temperature. These alloys are usually composed of gallium and indium (elements used in low energy lamps), tin and bismuth (materials used in constructions). The ratio and nature of elements in liquid alloys generate extraordinary phenomena on the surface of liquid metals which have been rarely explored to date and …
Home-grown semiconductors for faster, smaller electronics
‘Growing’ electronic components directly onto a semiconductor block avoids messy, noisy oxidation scattering that slows and impedes electronic operation. A UNSW study out this month shows that the resulting high-mobility components are ideal candidates for high-frequency, ultra-small electronic devices, quantum dots, and for qubit applications in quantum computing. Smaller means faster, but also noisier Making computers faster requires ever-smaller transistors, …
Where are they now? Life Post-FLEET with Paul Atkin
Talk to as many people as possible about your future career Stay open to new career directions Hi, I’m Paul Atkin. If we didn’t meet during my time as a FLEET scientist, we may have met more recently in my new life as a sales guy. If we haven’t met yet, I sincerely apologise and strongly suggest we meet for …
New 2D research hub features FLEET talent
A new ARC Research Hub highlighting the role of novel and 2D materials in emerging technologies in fields such as energy storage, purification and printed electronics features FLEET talent amongst its team. The ARC Research Hub for Advanced Manufacturing with 2D Materials (AM2D) will be led by Prof Mainak Majumder (Monash Department of Mechanical Engineering). Two FLEET Chief Investigators are amongst …
Transforming the layered ferromagnet Fe5GeTe2 for future spintronics
Realizing in-situ magnetic phase transition in metallic van-der-Waals magnet Fe5GeTe2 via ultra-high charge doping A RMIT-led international collaboration published this week has achieved record-high electron doping in a layered ferromagnet, causing magnetic phase transition with significant promise for future electronics Control of magnetism (or spin directions) by electric voltage is vital for developing future, low-energy high-speed nano-electronic and spintronic devices, …
Inducing and tuning spin interactions in layered material by inserting iron atoms, protons
Controlling Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interaction (DMI) in chiral magnet iron-doped tantalum-sulfide by proton intercalation Magnetic-spin interactions that allow spin-manipulation by electrical control allow potential applications in energy-efficient spintronic devices. An antisymmetric exchange known as Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interactions (DMI) is vital to form various chiral spin textures, such as skyrmions, and permits their potential application in energy-efficient spintronic devices. Published this week, a Chinese-Australia …
Tools of the Trade: Iolanda Di Bernardo explains XPS depth profiling for Nature series
X- ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) is used for material characterization, providing quantitative information on the chemical composition of materials by identifying the type of elements that are present (nowadays, with a detection limit in the range of one part per thousand). XPS also allows the identification of the chemical state of the elements – such as the types of bonds …
Liquid metals spin-off launched
The Liquid-metals spin-off company Liquid Metal Plus (LM+) initiated in 2020 with FLEET investigators Kourosh Kalantar-Zadeh (UNSW) and Dr Torben Daeneke (RMIT), together with Dorna Esrafilzadeh (UNSW), was launched in April 2021. Pushing print on flexible touchscreens Climate rewind: turning CO2 back into coal The company has two areas of focus, with the unifying theme being application of liquid-metal technologies …
Harnessing socially-distant molecular interactions for future computing
Could long-distance interactions between individual molecules forge a new way to compute? Interactions between individual molecules on a metal surface extend for surprisingly large distances – up to several nanometers. A new study, just published, of the changing shape of electronic states induced by these interactions, has potential future application in the use of molecules as individually addressable units. For …
Nano-thin piezoelectrics advance self-powered electronics
A new type of ultra-efficient, nano-thin material could advance self-powered electronics, wearable technologies and even deliver pacemakers powered by heart beats. The flexible and printable piezoelectric material, which can convert mechanical pressure into electrical energy, has been developed by an Australian research team led by RMIT. It is 100,000 times thinner than a human hair and 800% more efficient than …
Zebra stripes, leopard spots and other patterns on the skin of frozen metal alloys that defy conventional metallurgy
“Stripy zebra, spotty leopard, …”. Kids never become bored pinpointing animals based on their unique body patterns. While it is fascinating that living creatures develop distinct patterns on their skin, what may be even more mysterious is their striking similarity to the skin of frozen liquid metals. Pattern formation is a classic example of one of nature’s wonders that scientists …
Liquid metals come to the rescue of semiconductors
Moore’s law is an empirical suggestion describing that the number of transistors doubles every few years in integrated circuits (ICs). However, Moore’s law has started to fail as transistors are now so small that the current silicon-based technologies are unable to offer further opportunities for shrinking. One possibility of overcoming Moore’s law is to resort to two-dimensional semiconductors. These two-dimensional materials …
Next-generation multi-state data storage: leaving binary behind
International collaboration reviews future data-storage technology that steps ‘beyond binary’, storing more data than just 0s and 1s Electronic data is being produced at a breath-taking rate. The total amount of data stored in data centres around the globe is of the order of ten zettabytes (a zettabyte is a trillion gigabytes), and we estimate that amount doubles every couple …
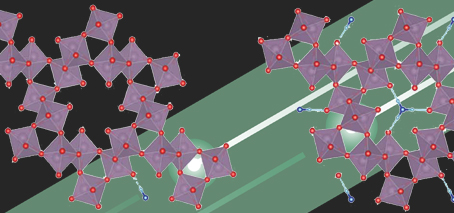
Using protons to tune interlayer forces in van-der-Waals materials
Interlayer coupling in vdW material Fe3GeTe2 successfully increased by insertion of protons A Chinese-Australian collaboration has demonstrated for the first time that interlayer coupling in a van der Waals (vdW) material can be largely modulated by a protonic gate, which inject protons to devices from an ionic solid. The discovery opens the way to exciting new uses of vdW materials, …
Liquid metal synthesis for better piezoelectrics: atomically-thin tin-monosulfide
Record output power obtained from piezoelectric, atomically-thin material Remarkable synthesis advance for materials such as tin-monosulfide (group IV monochalcogenides), which are predicted to exhibit strong piezoelectricity Potential materials for future wearable electronics and other motion-powered, energy-harvesting devices RMIT-UNSW collaboration applies liquid-metal synthesis to piezoelectrics, advancing future flexible, wearable electronics, and biosensors drawing their power from the body’s movements. Materials such …
FLEETs Kourosh Kalantar-zadeh awarded prestigious prize
FLEET CI Professor Kourosh Kalantar-zadeh (UNSW Sydney) has been awarded the prestigious 2020 Robert Boyle Prize for Analytical Science by The Royal Society of Chemistry. Prof Kalantar-zadeh is recognised for his significant influence across multiple fields of engineering. Contributions to society coming from his research across multiple disciplines include new innovative pollution sensors, transistors, medical devices and optical systems. Many …
Liquid metals break down organic fuels into ultra-thin graphitic sheets
For the first time, FLEET researchers at UNSW, Sydney show the synthesis of ultra-thin graphitic materials at room temperature using organic fuels (which can be as simple as basic alcohols such as ethanol). Graphitic materials, such as graphene, are ultra-thin sheets of carbon compounds that are sought after materials with great promises for battery storage, solar cells, touch panels and …
Studying phonon-polaritons in hBN
Phonon-polaritons in layered crystals have peculiar properties where they occur at the boundary between materials. In a new study led from UNSW, phonon-polaritons were studied in thin-layer hexagonal boron nitride (hBN) by combined scattering-type scanning near-field optical microscopy (s-SNOM) and Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy. Prof Kourosh Kalantar-zadeh’s multidisciplinary group at UNSW combined scattering-SNOM single-wavelength imaging and broadband scattering IR …
Nano-thin flexible touchscreens could be printed like newspaper
Researchers have developed an ultra-thin and ultra-flexible electronic material, able to be printed and rolled out like newspaper, for the touchscreens of the future. The touch-responsive technology is 100 times thinner than existing touchscreen materials and so pliable it can be rolled up like a tube. To create the new conductive sheet, an RMIT University-led team used a thin film …
Collaboration unlocks new magnetic properties for future, faster, low-energy spintronics
• RMIT–UNSW collaboration combines theory, experimental expertise • ‘Spintronic’ applications promise faster, more efficient computing • New magnetic properties of 2D Fe3GeTe2 (FGT) discovered A theoretical–experimental collaboration across two FLEET nodes has discovered new magnetic properties within 2D structures, with exciting potential for researchers in the emerging field of ‘spintronics’. Spintronic devices use a quantum property known as ‘spin’, in …
Meet molybdenum, an acid-free route to future Hydrogen power?
Molybdenum based compounds could provide key to hydrogen production for future zero-emissions energy RMIT/Monash collaboration opens promising route towards alkaline hydrogen production A FLEET study combining experimental expertise at RMIT with theoretical modelling at Monash University opens a new route towards efficient, cost-effective production of hydrogen. Researchers discovered that ammonium-doped, hexagonal molybdenum oxide (MoO3) displays extremely promising electronic and material …
Using disorder to build new materials for low-energy electronics: welcome new FLEET AI Julie Karel
Dr Julie Karel conducts research at the intersection of materials science and condensed matter physics to develop new materials for emerging low-energy nanoelectronic and magnetoelectronic devices. Originally from the US, Julie developed new thermal interface materials to improve mobile-device performance at Intel, and was a postdoctoral researcher at the Max Planck Institute in Germany. In materials design, Julie uses complete …
Researchers discover directional, long-lived nanolight in 2D material
An international team led by researchers from Soochow University (Suzhou, China), Monash University (Melbourne, Australia), University of Oviedo (Asturias, Spain), and CIC nanoGUNE (San Sebastián, Spain) have discovered squeezed light (‘nanolight’) in the nanoscale that propagates only in specific directions along thin slabs of molybdenum trioxide – a natural anisotropic 2D material. Besides its unique directional character, this nanolight lives …
Pushing ‘print’ on large-scale piezoelectric materials
First ever large-scale 2D surface deposition of piezoelectric material Simple, inexpensive technique opens new fields for piezo-sensors & energy harvesting Researchers have developed a revolutionary method to ‘print’ large-scale sheets of two dimensional piezoelectric material, opening new opportunities for piezo-sensors and energy harvesting. Importantly, the inexpensive process allows the integration of piezoelectric components directly onto silicon chips. Until now, no …
Centre collaboration combines material expertise
FLEET RMIT—UNSW collaboration measuring transport properties of van der Waals heterostructures FLEET PhD Cheng Tan (RMIT) visited UNSW’s labs in May to perform magnetic coupling measurements on 2D ferromagnetic crystals. The visit was reciprocated this month with FLEET Research Fellow Feixiang Xiang (UNSW) visiting RMIT to construct van der Waals structures for studying of 2D topological systems. This collaboration between …
Thinner is better: van der Waals (vdW) material shows the right stuff at 200 nanometres
The unusual electronic and magnetic properties of van der Waals (vdW) materials, made up of many ‘stacked’ 2D layers, offer potential for future electronics, including spintronics. In a recent study, FLEET researchers at RMIT found that one promising candidate material, Fe3GeTe2 (FGT), fits the bill – provided it’s created in layers only 200 millionths of a millimetre in thickness. This …
FLEET’s Qiaoliang Bao a champion of Australian nanotech
FLEET-nano collaboration recognised: Congratulations to Qiaoliang Bao, 2018 ANFF-VIC Technology Fellow Qiaoliang Bao works at the nanoscale, trapping photons in atomically-thin, two-dimensional materials, where high binding energies create a quantum state known as a superfluid. The aim is a new generation of superfluid transistors that will ‘switch’ using much less energy than conventional electronics. Such work requires access to the …
Custom, nanoscale structures on demand at RMIT
“Endless” possibilities for custom nanotech design FLEET’s research to achieve zero-dissipation electrical current depends on the design of key nanoscale structures. Within FLEET, nano-device fabrication is coordinated via Enabling technology B, which links each of the research themes. In 2017, Theme B leader Lan Wang, and PhD student Cheng Tan, developed a method to build such nanoscale structures, required to achieve zero-dissipation …
Ingestible smart pill recognised
Kourosh Kalantar-zadeh’s ingestible smart pill could revolutionise prevention and diagnosis of gut disorders/disease, and make a significant difference to the health of as many as one in five Australians who suffer gut disorders. This month the technology won the prestigious 2017 IEEE Sensors Council achievement award in the field of sensors. Read more at RMIT. At RMIT,Prof Kalantar-zadeh is Director …
Materials one atom thick & nanotransistors: FLEET features in nano edition
FLEET features in this month’s annual ‘nano’ edition of the Australian Manufacturing Tech magazine. The article looks at growth of atomically thin and other novel materials and nanofabrication, with a particular focus on partnerships. Atomically thin material projects presented include semiconductor fabrication at RMIT University (Lan Wang) and the University of Wollongong (Xiaoliang Wang) and molecular beam epitaxy (Mark Edmonds …
Band alignment at semiconductor junction looking good for low-resistance contacts
The future of ultra-low resistance semiconductor junctions in novel low-energy electronics is looking good after a recent study took a very close look at band alignment. FLEET is using two-dimensional materials in the search for new electronics devices that will carry electrical current without losing the significant energy dissipated in current, silicon technology. The new electronic devices developed at FLEET …