A Meet FLEET innovation-and-industry event poster
The Challenge
The International Energy Agency (IEA) has identified computing, and in particular data centres, as a rising source of energy usage.
Energy generation continues to be dominated by the burning of fossil fuels such as gas, coal and oil – all of which produce carbon dioxide (CO2 ), which contributes to the Greenhouse effect and climate change.
The Solution
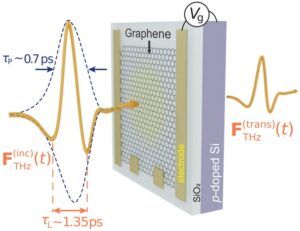
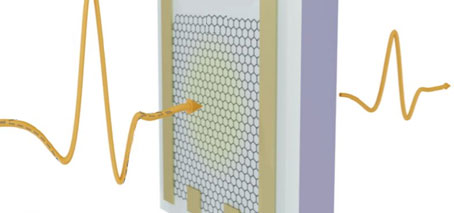
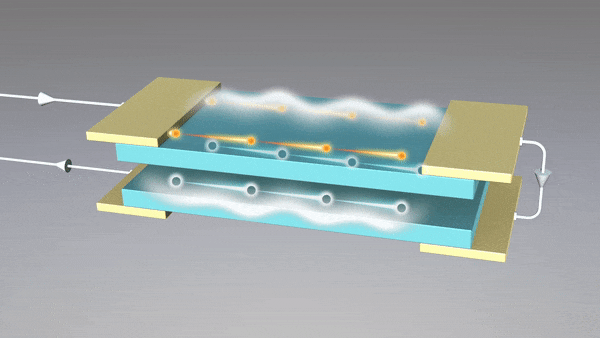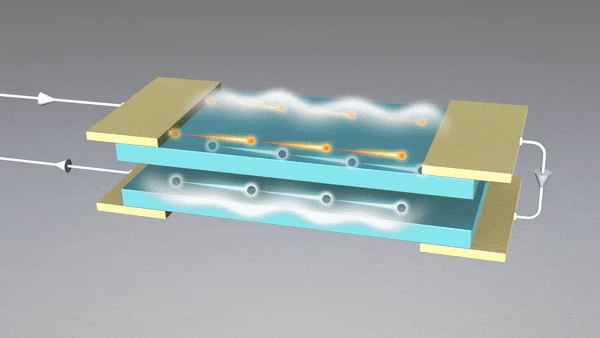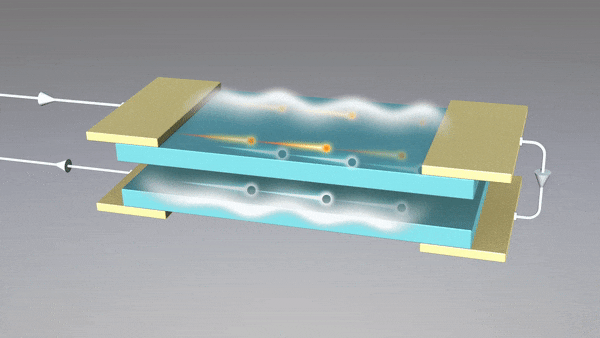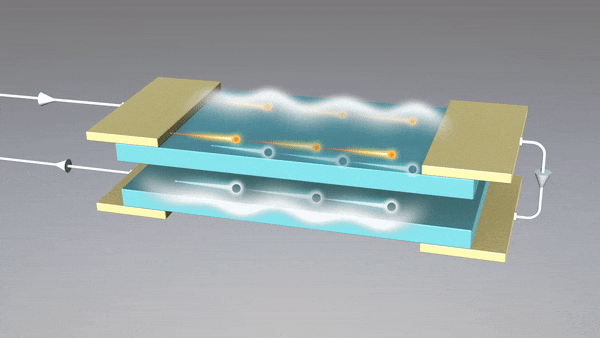
The fabricated device structure, with a graphene layer on a silica/p-doped back-gate electrode, modulates incoming quasi-single-cycle THz pulses using the backgate. The amplitude and phase of the transmitted THz pulses also provides information about changes in AC conductivity
Our solution involves the use of the Dirac semimetal graphene on a silicon substrate with a back gate electrode.
This material can be switched between high and low conductivity phases through the application of either a conventional back-gate electrode and a DC potential, or at THz frequencies using an applied THz pulse.
Key Benefits
- The generation of IP on a well-established 2D material
- Demonstrated control of conductivity with a DC field
Development Stage
- Technology concept in final stages
- Seeking strategic partners
Brief Description & Differentiation
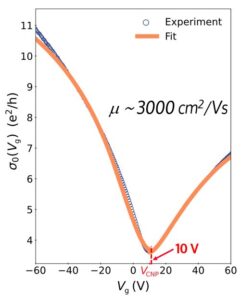
Graphene can be gated to the minimum of conductivity (charge neutrality point, CNP) at room temperature and under ambient atmosphere
Our system and approach aims to move beyond both conventional transistor designs and the low switching speeds which can be achieved with electrode-based gates. We envision transistors in which the electric field from a gate electrode is instead replaced by optical gate pulses from lasers with switching speeds in the THz regime.
We have developed fabrication techniques that allow for graphene to be gated to the charge-neutrality point (CNP), a minimum of conductivity, at room temperature and under ambient atmosphere. Using this well-established 2D material we have developed a device using well-established nanolithography techniques where the conductivity can be controlled. Further demonstration of conductivity control at THz frequencies is ongoing.
Intellectual Property
None
Key Publications
- T.P. Nguyen, et. al., (in preparation)
More information
- Contact Dr Gary Beane, Monash University, gary.beane@monash.edu
- Contact A/Prof Agustin Schiffrin, Monash University, agustin.schiffrin@monash.edu