Engage
See news from around FLEET, below
Catch up on all past issues of FLEET News newsletter
FLEET News
This month’s ARC funding round saw FLEET research and researchers across five universities awarded additional funding. Across eight separate grants, almost $4.6m new research funding went to projects and facilities led by or involving FLEET researchers or directly contributing to FLEET’s search to develop ultra-low energy electronics and boost related areas of research. Two projects in particular will be key …
FLEET’s Monash labs recently hosted a tour by members of the Victorian branch of the Australian Institute of Physics, the country’s leading body for physics advocacy and support. The tour included the experimental laboratories of FLEET Chief Investigators Michael Fuhrer, Agustin Schiffrin, Kris Helmerson and Qiaoliang Bao. Members saw where: Michael Fuhrer grows atomically-thin (2D) materials in the lab using …
UNSW researchers solve a 10-year-old mystery in the way nanoscale transistors work. Half of all the transistors in your iPhone use positively-charged ‘holes’, rather than negatively-charged electrons to operate. At university, we teach undergraduates that holes are quasiparticles, basically ‘missing electrons’ – a bit like the bubble in a spirit level, or the missing chair in a game of musical …
A variety of methods exist to deposit atomically-thin (two-dimensional) crystals. But large-scale deposition has remained a challenge. However a recent RMIT-led study has found success with a new technique with potential to open new doors for two-dimensional semiconductors. The discovery has been described as a ‘once-in-a-decade’ advance. The new technique introduces room-temperature liquid metals (gallium-based) as a successful reaction environment …
Public talk 30 November All are welcome to a public talk at Swinburne University of Technology (Hawthorn) at 7PM on Thursday 30 November. Prof Ketterle will discuss Bose-Einstein condensates, in which atoms are cooled to temperatures a billion times colder than outer space, and matter behaves as a wave, “marching in quantum lockstep”. These forms of ultra-low temperature matter, …
Where can your PhD take you? And how can you maximise your potential future? A group of STEM PhDs and higher degree researchers heard about career options post-PhD at a forum last month, run by FLEET at Monash University. The assembled panel of academics, entrepreneurs, business development and research managers shared their own diverse career journeys and top tips on …
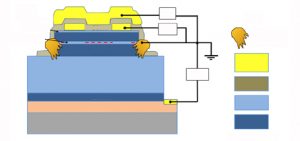
FLEET’s mission to create ultra-low energy electronics depends on an improved fundamental understanding of the electronic structure of atomically-thin, two-dimensional materials. We need to understand how electrons in the material interact with each other and also how they move and scatter through the crystal lattice. FLEET researchers using the vacuum ultraviolet the UV beamline 10.0.1 (HERS) at the Advanced Light …
Kourosh Kalantar-zadeh’s ingestible smart pill could revolutionise prevention and diagnosis of gut disorders/disease, and make a significant difference to the health of as many as one in five Australians who suffer gut disorders. This month the technology won the prestigious 2017 IEEE Sensors Council achievement award in the field of sensors. Read more at RMIT. At RMIT,Prof Kalantar-zadeh is Director …
FLEET Director Michael Fuhrer spoke today with science show Einstein a gogo on 3RRR about energy use in information and communications technology (ICT), limits to our ability to squeeze more efficiency out of traditional silicon-based technologies, and the alternatives that FLEET is pursuing, including topological materials and atomically-thin materials. Listen
From Monash University Insider (staff only) While a smartphone or home PC itself doesn’t burn too much energy, a tremendous amount of electricity is consumed in the massive data centres (or ‘server farms’) that keep us all connected via the net. A new, ARC-funded research centre aims to address the growing computing energy challenge using materials that are just one …
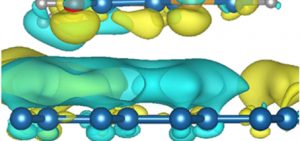
There is considerable excitement about graphene-based biosensors. In particular, the material’s unique structure and electronic properties offers great potential for rapid, reliable DNA/RNA sensing and sequencing. To date, this potential has been checked by a lack of fundamental understanding of graphene−nucleobase interactions and the origin of measured molecular fingerprints. A recent study has defined key interactions as DNA/RNA nucleobases are …
Monash University’s recent open day provided a great opportunity to explain FLEET to a large audience. The FLEET zone in the School of Physics and Astronomy area allowed for hands-on demonstrations, while lab tours provided a closer look at the research and FLEET director Michael Fuhrer presented a talk on the big picture challenges of energy use in global computing. …
FLEET features in this month’s annual ‘nano’ edition of the Australian Manufacturing Tech magazine. The article looks at growth of atomically thin and other novel materials and nanofabrication, with a particular focus on partnerships. Atomically thin material projects presented include semiconductor fabrication at RMIT University (Lan Wang) and the University of Wollongong (Xiaoliang Wang) and molecular beam epitaxy (Mark Edmonds …
FLEET research has been highlighted at an important conference in Würzburg, Germany. Eli Estrecho, a PhD student in Elena Ostrovskaya’s group at ANU, won the 1st “Gold” award (and €500) for the best poster presentation entitled ‘Single-shot imaging of exciton-polariton condensates’ and David Colas, a Postdoctoral Fellow in Matt Davis’ group won one of the 3rd “Bronze” prizes for his poster …
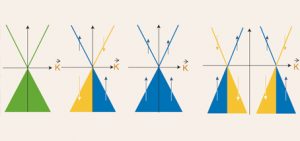
A University of Wollongong study has tightened the search for materials that would allow for ultra-fast, ultra-low energy ‘spintronic‘ electronics with no wasted dissipation of energy from electrical conduction. Spintronics is an emerging field of electronic study in which the ‘spin’ of electrons (their intrinsic angular momentum) is used in addition to their charge. Conventional electronics and information technology are …